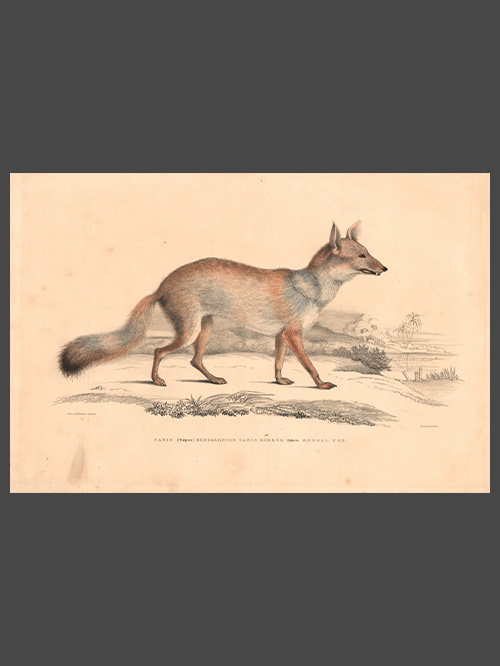
by W H Fitch from John Eliot Howard’s
‘The Quinology of the East Indian Plantations’
original hand coloured lithograph
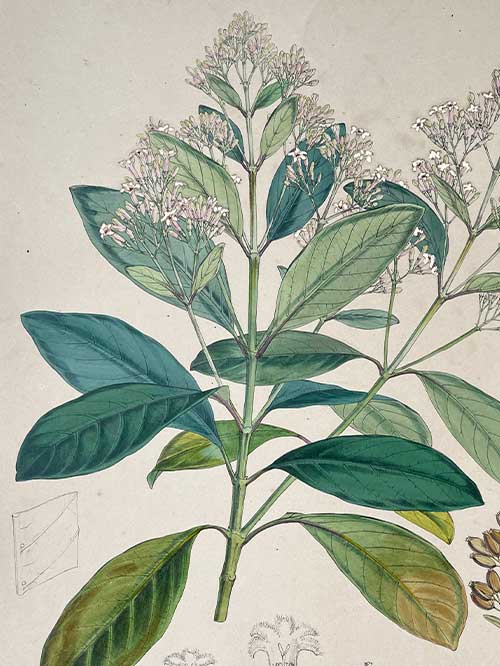
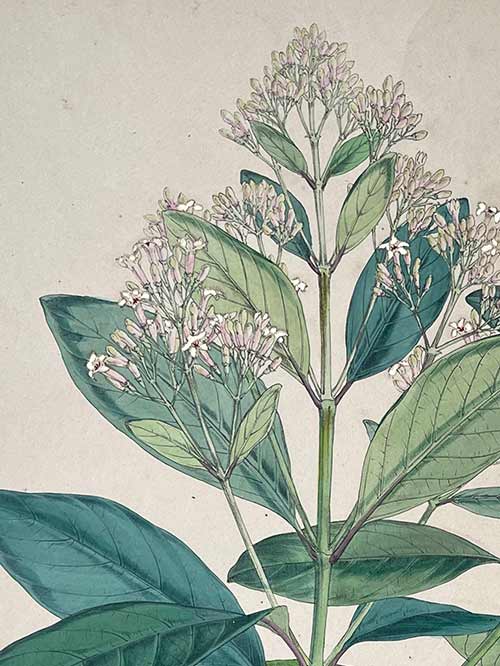
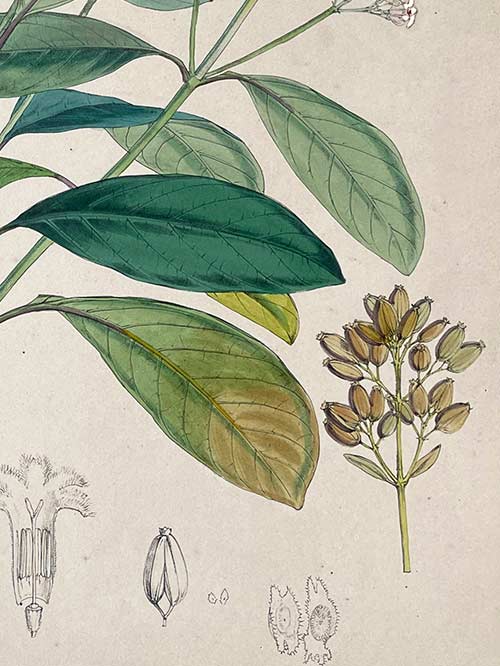
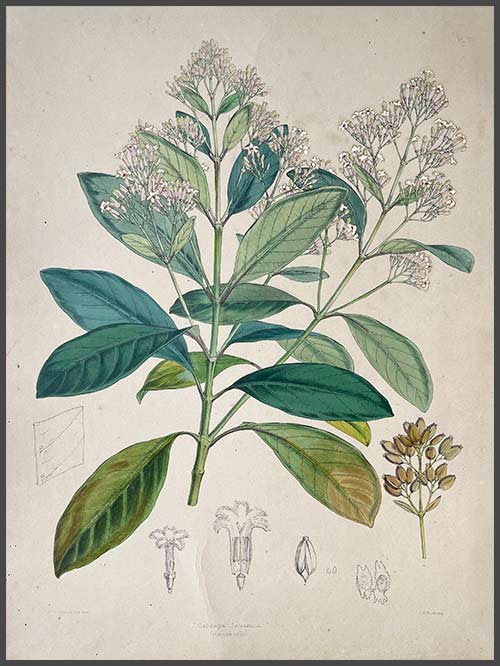
The tree bark of the Cinchona tree contains quinine, an alkaloid used to treat malaria. Malaria was a major health concern for the colonial administration in India and the first cinchona plantation was established in 1860 in the Nilgiri Hills due to its suitable climate and soil. Over the next few years, several other plantations were established in the region, including at Coonoor, Kotagiri, and Ooty. By the early 20th century, the Indian cinchona plantations had become one of the largest producers of quinine in the world, supplying not only India but also other parts of the British Empire.
‘The Quinology of the East Indian Plantations’ by John Eliot Howard (1807-1883) is a continuation of Benjamin Moseley’s earlier book on the same subject, and provides an updated account of the cultivation and use of quinine in the East Indian plantations during the 19th century and its introduction into India. Howard’s book includes detailed descriptions of the different species of cinchona trees, as well as the various methods used to extract and prepare quinine. He also discusses the economic and political implications of the quinine trade, which had become a major industry in the region by the mid-19th century. Howard received the thanks of Her Majesty’s Government in 1873 for The Quinology of the East Indian Plantations.
Framed Size (cms): 65(H) x 54(W)
Framed Size (inches): 25.5(H) x 21.5(W)
Print Size (cms): 45.75(H) x 34.25(W)
Print Size (inches): 18(H) x 13.5(W)